Introduction
Ecofact are incredible remnants of the past that offer valuable insights into ancient ecosystems, climates, and civilizations. These natural wonders offer a window into the evolution of our planet and the existence of extinct species. This post explores ten astounding ecofacts that will astound you as we dig into the astounding world of ecofacts.
Ecofact 1: Ancient Remains of Giant Ground Sloths
The discovery of ancient remains belonging to the giant ground sloth has uncovered countless mysteries about these colossal creatures. These giant sloths, which formerly roamed the Earth thousands of years ago, were up to 20 feet long and many tonnes in weight. Their fossils have been discovered in numerous locations around the globe, demonstrating their former extensive distribution.
Palaeontologists have learned more about the sloths’ environment, behaviour, and eventual extinction by examining their bones. They are a striking illustration of the vulnerability of Earth’s ecosystems because it is thought that a combination of climate change and human engagement caused their extinction.

Ecofact 2: Petrified Forests: Frozen in Time
Nature’s incredible process of petrification has left us with astonishing petrified forests that provide a glimpse into ancient landscapes. Petrification occurs when organic matter is gradually replaced by minerals, resulting in the transformation of wood into stone.
These petrified wood forests hold a wealth of secrets within their ancient rings, offering valuable clues about past climates and the species that once thrived there. By meticulously studying the preserved tree rings, scientists can gather information about rainfall patterns, temperature fluctuations, and even the occurrence of major geological events.

Ecofact 3: Amber: Time Capsules of Ancient Life
Amber, often referred to as “nature’s time capsules,” encapsulates small organisms and insects within its golden embrace. This fossilized tree resin provides an unparalleled opportunity for scientists to study ancient life forms in astonishing detail. Insects trapped in amber serve as snapshots frozen in time, preserving delicate anatomical features that would otherwise be lost to the ages.
By examining these perfectly preserved organisms, researchers can gain insights into prehistoric ecosystems, the evolution of species, and even ancient diseases that impacted flora and fauna.

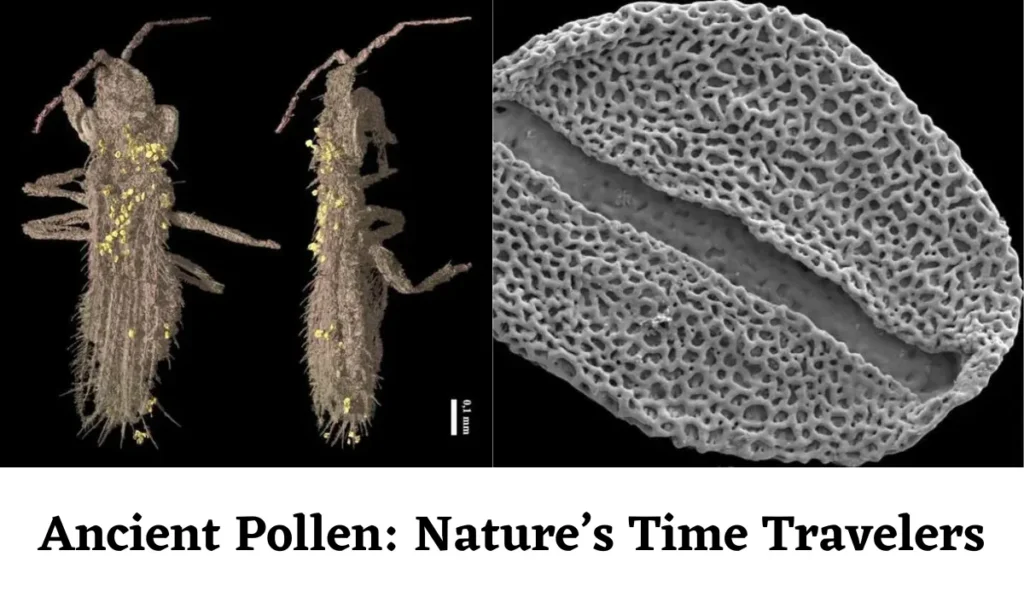
Ecofact 4: Ancient Pollen: Nature’s Time Travelers
Pollen grains are master time travelers, journeying through the winds and settling in various environments, where they accumulate over time. By studying ancient pollen samples preserved in sediments, scientists are unlocking the secrets of past ecosystems.
These minute grains contain a wealth of knowledge that enables scientists to reassemble ancient vegetation, follow the migration of plant species, and obtain a better understanding of how climate change has impacted our world over time. Ancient pollen analysis offers crucial insights into the interwoven web of life and can even help predict the effects of climate change in the future.
Ecofact 5: Mummified Animals: Preserved for Posterity
Mummification, traditionally associated with ancient Egyptian culture, can also occur naturally, providing us with exceptional insights into the past. From the frozen remains of mammoths to the desiccated bodies of desert-dwelling creatures, mummified animals offer an astonishing glimpse into ancient ecosystems and civilizations.
These preserved specimens provide scientists with valuable information about animal physiology, diet, and even the potential presence of diseases in the past. By studying these remarkable mummies, researchers bridge the gap between past and present, unraveling the mysteries of our natural world.

Ecofact 6: Fossilized Footprints: Tracking Prehistoric Life
While fossils typically consist of preserved bones or shells, fossilized footprints offer a unique perspective on ancient life. Through a combination of sedimentation and fossilization processes, the impressions left by prehistoric creatures’ feet have been preserved, allowing us to track their movements and behavior.
By analyzing these fossil footprints, scientists can determine the size of the animal, its locomotion style, and even potential social interactions. Walking in the footsteps of these ancient creatures, we gain a deeper understanding of their existence and the ecosystems they thrived in.

READ MORE – 1 week or Months | How Long Is Dig Season In Egypt – Know Details
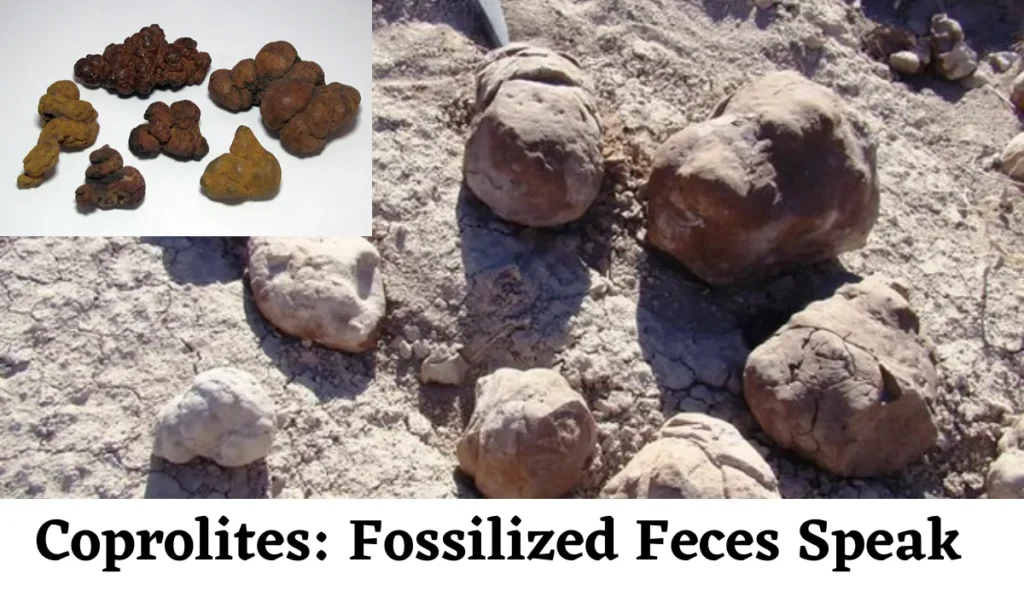
Ecofact 7: Coprolites: Fossilized Feces Speak Volumes
Among the curious, eco facts that reveal intriguing details about past organisms, coprolites take center stage. These fossilized feces, once scorned as repugnant remnants, are now celebrated as informative relics. Analyzing coprolites provides valuable insights into ancient diets, the interactions between species, and the structure of prehistoric ecosystems.
By studying the chemicals and remains within these fossilized droppings, scientists can reconstruct the diets and lifestyles of organisms long gone, glimpsing a world that was once teeming with life.

Ecofact 8: Preserved Prehistoric Plants: Ancient Green Thumb
The remarkable preservation of prehistoric plants offers us a vivid snapshot of ancient flora, helping us to understand the diverse ecosystems that existed millions of years ago. Fossilized leaves, seeds, and even flowers provide crucial evidence of past plant life, giving scientists clues about plant adaptations, evolutionary relationships, and climate conditions.
By analyzing these exquisitely preserved specimens, researchers piece together the botanical tapestry of our planet’s history, painting a picture of the verdant landscapes that have come before us.

Ecofact 9: Ice Cores: Unlocking Earth’s Climate History
Frozen within the immense glaciers of our planet, ice cores are extraordinary time capsules that hold vital information about Earth’s climate history. These cylindrical ice samples, extracted from polar regions or glaciers, provide scientists with a chronicle of ancient atmospheric conditions.
By examining the layers within ice cores, researchers extract tiny air bubbles, dust particles, and even pollutants, uncovering past climate patterns and changes. Ice cores reveal the historical impact of human activities on our environment, offering critical insights into climate change, air quality, and the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems.

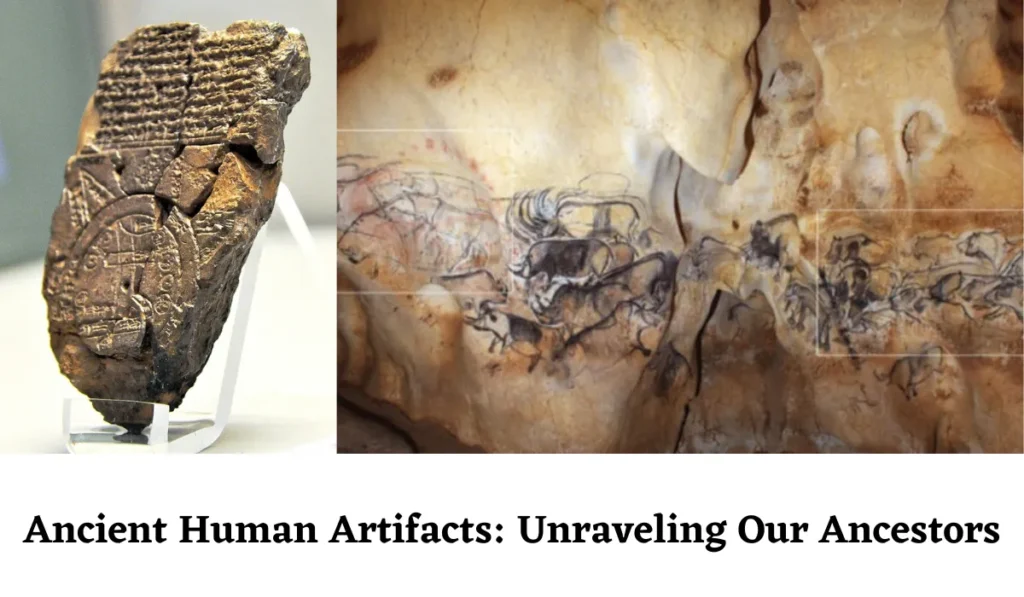
Ecofact 10: Ancient Human Artifacts: Unraveling Our Ancestors
Archaeological treasures left by our early ancestors offer profound insights into the lives and cultures of ancient civilizations. From cave paintings to intricately crafted tools and pottery, every artifact tells a story of our shared human heritage. These artefacts reveal priceless details about historic technologies, artistic expressions, cultural structures, and even the difficulties that our ancestors encountered.
By studying these magnificent artefacts, we may bridge the gap between our modern world and the world of our ancestors and get a greater understanding of the richness and complexity of human history.
Summary of Uncovered Ecofacts
The ten eco facts showcased in this article offer incredible windows into our planet’s past. From the remains of ancient giants to the frozen moments captured in petrified forests and amber, each eco fact carries its own unique significance. Scientists discover the mysteries of our natural world by exploring and comprehending these fascinating remnants, giving us important new information about the complex web of life and the forces that have shaped our planet.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How are eco facts different from artifacts?
Eco facts are natural remains or traces of past organisms, while artifacts are objects created or modified by humans.
Are there any eco facts that pose ethical concerns when studying?
While eco-facts are generally ethically sound to study, instances involving the disturbance of culturally or spiritually significant sites may pose ethical dilemmas.
How do eco-facts contribute to scientific research?
Eco-facts play a vital role in various scientific disciplines, including paleontology, archaeology, climatology, and ecology. They provide tangible evidence that aids in reconstructing our planet’s history and understanding its complex systems.
Can eco-facts help us predict future environmental changes?
By studying eco-facts and the patterns they reveal, scientists can gain critical knowledge about past environmental changes. This knowledge aids in predicting potential future scenarios and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Are there ongoing discoveries in the field of eco facts ?
Absolutely! Each new discovery brings with it the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the past. Ongoing research continues to uncover new eco-facts and shed light on mysteries that have long intrigued scientists and enthusiasts alike.
What are examples of ecofacts?
Organic remains such as animal bones, plant seeds, pollen, shells, and charcoal are examples of eco-facts.
What is the difference between an artifact and an ecofact?
Origin and human involvement are the fundamental distinctions between an artefact and an eco-fact. In contrast to an artefact, which is a creation of humankind with cultural significance, an eco-fact is a natural object or relic that includes information about the environment, such as plant or animal remains.
What is a ecofact in Archaeology?
An eco fact is a natural artefact or relic that has been uncovered at an archaeological site and is used to shed light on past ecosystems and how people interacted with them. Eco facts are important in the field of archaeology. Plant remains, animal bones, shells, charcoal, and other organic elements can all be considered eco facts.
Why are ecofacts important?
Eco facts are valuable in archaeology because they can reveal information about earlier habitats, human activities, subsistence practises, diet, trade, and the larger cultural context of a particular archaeological site. They support the study of human interactions with the environment, the rebuilding of ancient ecosystems, and the uncovering of daily life in those cultures
What are ecofacts also known as?
In certain instances, eco facts are also referred to as biofacts. Natural remnants discovered in archaeological environments are referred to as eco facts or biofacts interchangeably.
What is feature and eco fact?
An archaeological feature, such as a hearth, wall, or ditch, is a non-portable archaeological piece or building. On the other hand, an eco fact is a natural object or relic that offers knowledge about the environment. Eco facts are found inside features and are often related with natural processes, whereas features are typically associated with human actions.
What can we learn from ecofacts?
Eco-facts can offer archaeologists a plethora of knowledge. Researchers can gain knowledge about previous climatic conditions, flora, animal species, human food, hunting and gathering customs, agriculture, and trade networks by examining eco facts. They can also shed light on earlier human behaviours, such as the symbolic or ritual use of particular plants or animals.
Is ecofact the most important archaeological evidence?
Despite the fact that eco facts are essential archaeological evidence, it’s crucial to remember that no one sort of evidence is necessarily more significant than others. Our view of the past is influenced by a variety of archaeological evidence, such as artefacts, eco facts, features, and contexts. Depending on the research topics being addressed and the particular archaeological setting, each piece of evidence has a different level of significance.
Are human bones ecofacts?
Human remains can be regarded as eco facts, yes. Human bones are considered eco facts in the archaeological sense because they are organic remains that reveal details about previous human populations, burial customs, health, and demographics.
Conclusion
Uncovering and studying the remarkable ecofacts that our planet has preserved for us is a testament to our curiosity and desire to understand our natural and cultural heritage. From gigantic sloths to frozen forests, each ecofact offers a unique lens into a world that existed long before ours. Let us embrace these remnants of the past, exploring and appreciating the wonders they unveil, and strive to protect our planet’s intricate tapestry for future generations to discover and cherish.
Share to help